See DemandJump in Action
By embracing DemandJump's approach to SEO, we have been able to increase our organic rankings within just 2 weeks of implementing recommendations. This helped us see a 22% increase in organic search month-over-month.
Robert Jacko Vice President Digital Marketing @ Homage
DemandJump has become a crucial extension of our marketing team, providing game changing insights to fuel and propel all aspects of our digital marketing efforts. The DemandJump platform is a must have, we are seriously impressed.
Tim Lavinder Director of Ecommerce @ Hotsox
We used to spend hours looking for insights in dozens of tools and reports. Now we log into one place to find out what customers are doing and how to meet them where it matters most.
Zach Roop Digital Marketing Manager @ Dometic
We use DemandJump recommendations as our digital to-do list. We love going in and seeing the recommendations and knowing what to do next.
JoLynda Wilson Marketing Director @ IWC
Trusted by Brands Around the World
DemandJump Product Suite
Eliminate wasted time and spend. With DemandJump's content, insights, and attribution
you will know with certainty how to win by aligning your marketing to actual consumer behavior.
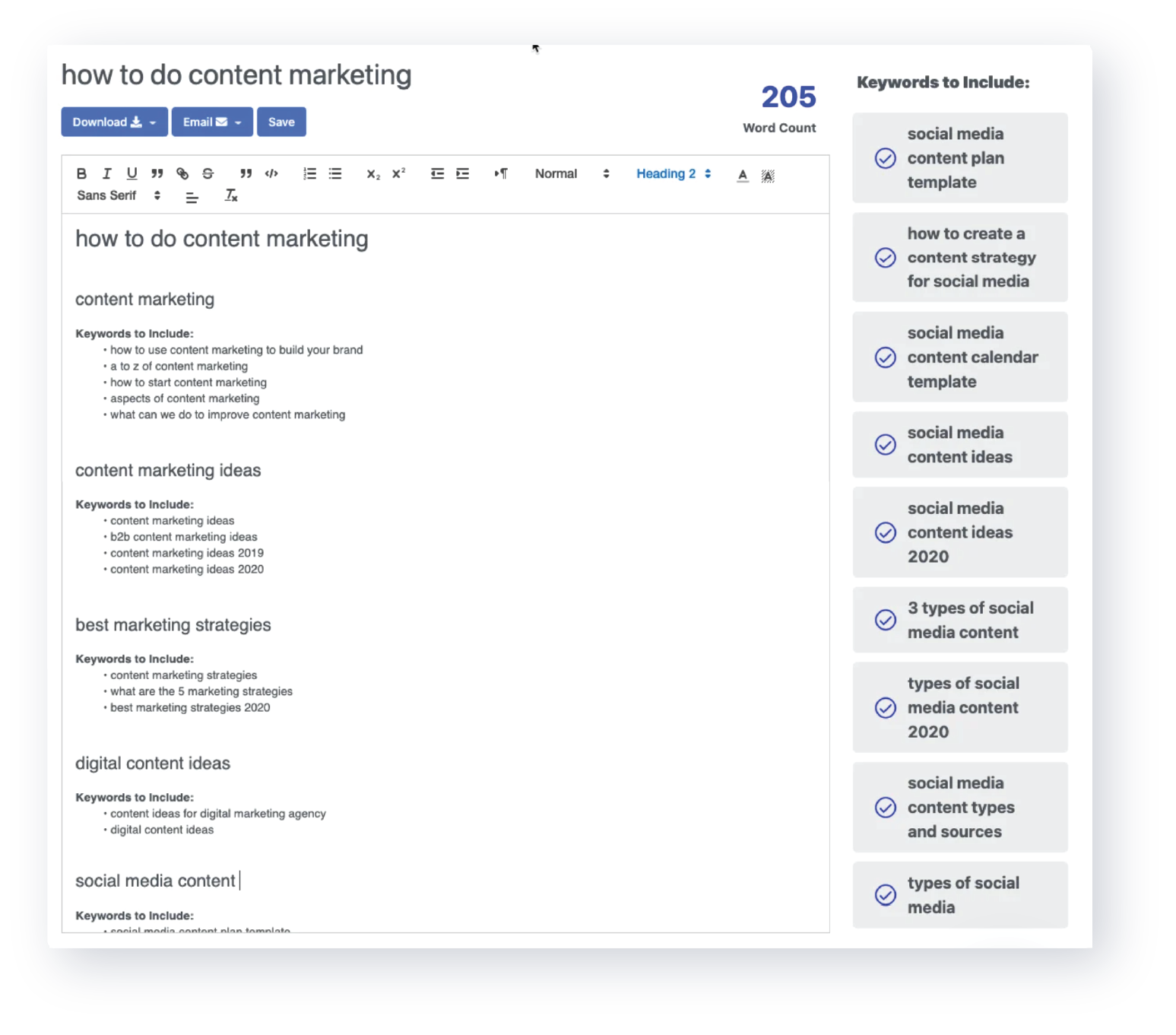
Content
DemandJump assembles the world’s data, creates networks of customer touchpoints around any topic or keyword, and tells you exactly what content to write, keywords to include, videos to produce, and much more.
Insights
Find out what your target audience cares about for any category, product, or topic, with the click of a button. Gain market share by aligning your marketing efforts to actual customer behavior.
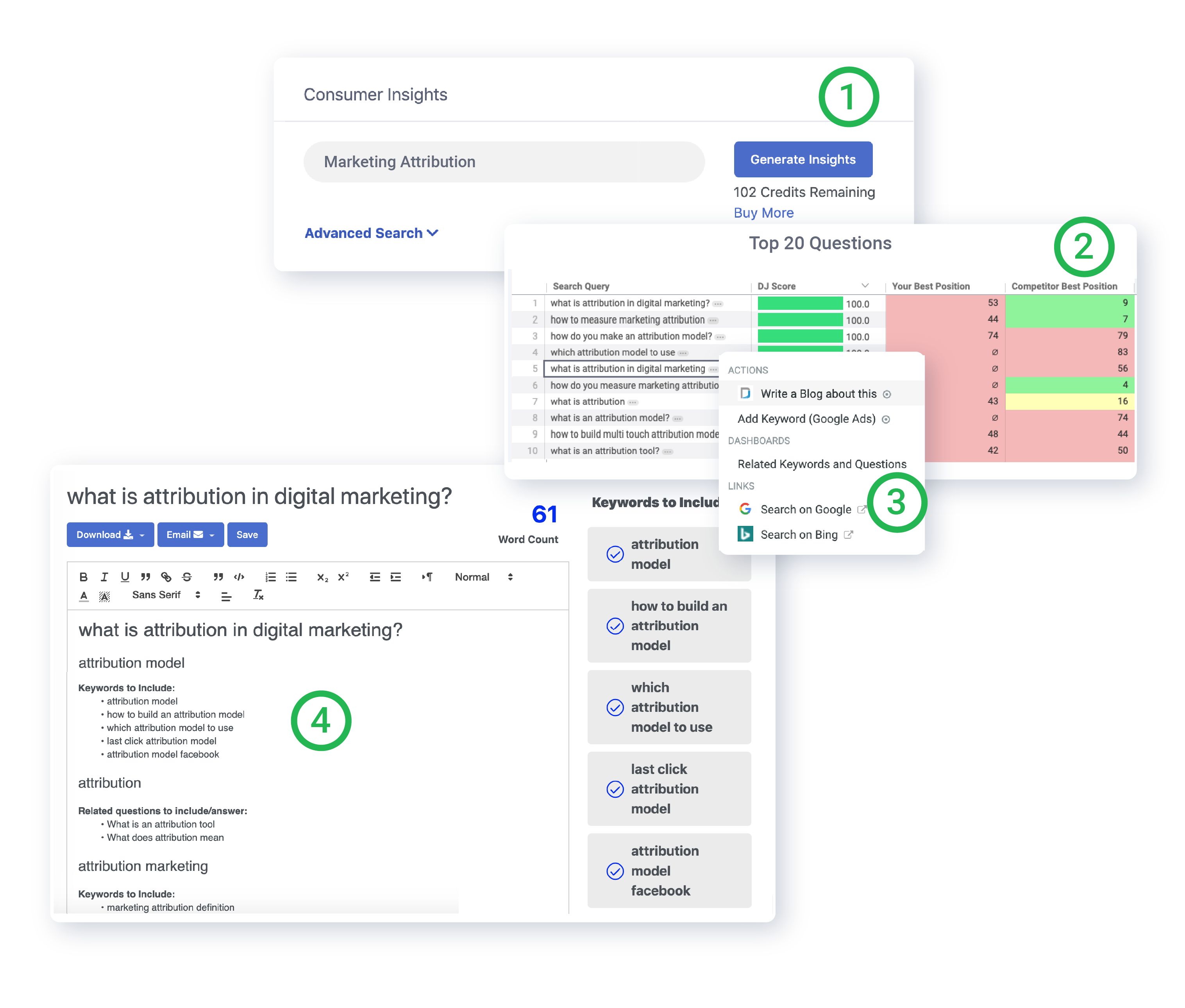
Attribution
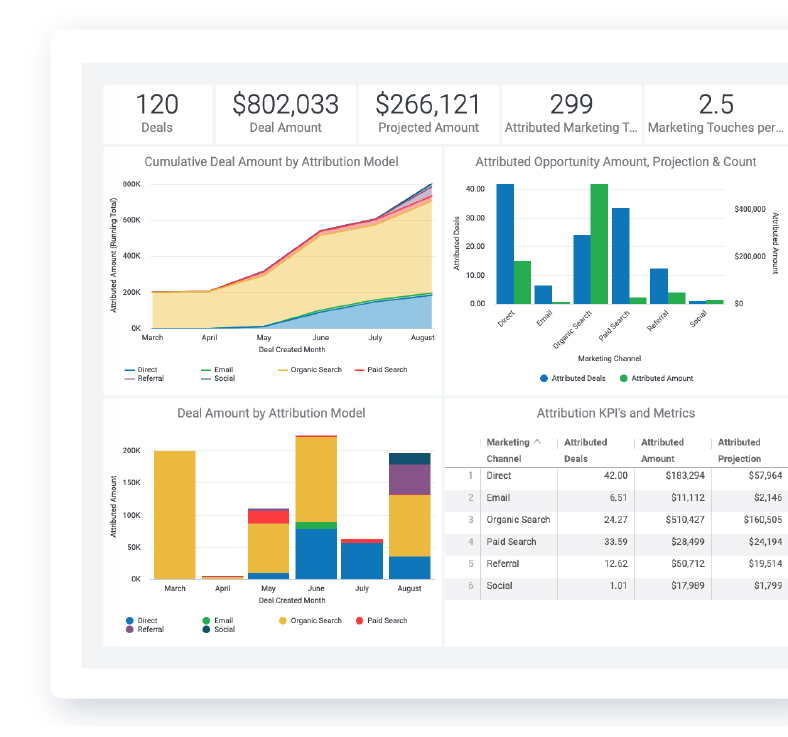
Eliminate wasted time and spend. With DemandJump's automated account-based attribution solution you will know with certainty which efforts are driving ROI.
See a Demo of DemandJump
In marketing, data plays a role in every aspect of the process. Today's advertising and marketing firms need to combine expertise in a few different disciplines. Psychology and the humanities are often the most noted because marketers work hard to understand the motivations of their audience and how to engage with them. However, these disciplines can only effectively move the business forward when decisions are backed by data.

The benefits of data are integral to marketing. Data science and data analytics are both in high demand. You may hear these terms being used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Here we'll largely discuss data analytics and data science as they relate to marketing but these two fields are in high demand across virtually every industry.
Data science is about building the processes to mine data. This field incorporates a few disciplines, such as computer science and AI. The data scientist works with devising programs and algorithms that find the right questions or queries in order to collect data. Data science is a larger, umbrella term used for all the work with data but it deals with the bigger questions. Data science helps you learn things you didn't realize were out there or discover what types of questions you should be asking in the first place.
Data analytics is a more finite practice. In data analytics, the analyst uses sets of data in order to find answers and actionable consumer insights. In data analytics, you use the data to answer questions or fix pain points that you know about. The analytics are set to capture precise information that can help businesses improve processes.
Big Data in Marketing
The benefits of data in business can't be understated. You use data to understand the projections in the industry, find out more about your ideal audience, assess your revenue cycle management process, and understand your competition. In real terms, there's no area of your business where data should not be used extensively. The data gives you concrete evidence to drive decision-making.
Sources of data are plentiful and it's an important aspect of the model for every size business. Digital data collection methods might include the analytics from web properties, campaigns through social media, email campaign analytics, and third party data, to name a few. Companies also make use of reporting options through their content marketing and management systems. All of this is data.
Once these different aspects of the company were contained in silos. Marketing and sales had their own individual information. Finance was separate. Even in smaller companies, the information was rarely shared or looked at outside the specific departments where the data was collected. Current thought leaders have found that better insights can be developed with more access to information, both inside the company and on a wider scale.
This is often the definition of big data. There are a few ways to explain big data vs data, but big data is usually categorized as information collected through many sources and where there’s so much of it that it can’t be reasonably analyzed with simple analysis. It's not necessarily called "big" because there is an abundance of information, though there might be. Big data is more about collecting and making use of the information that allows you a fuller picture of your company, the industry, and the consumer. For smaller companies, the ability to look at the whole market, pinpoint the ideal customer, and analyze individual performance metrics is essential for success in a market space with larger competitors.
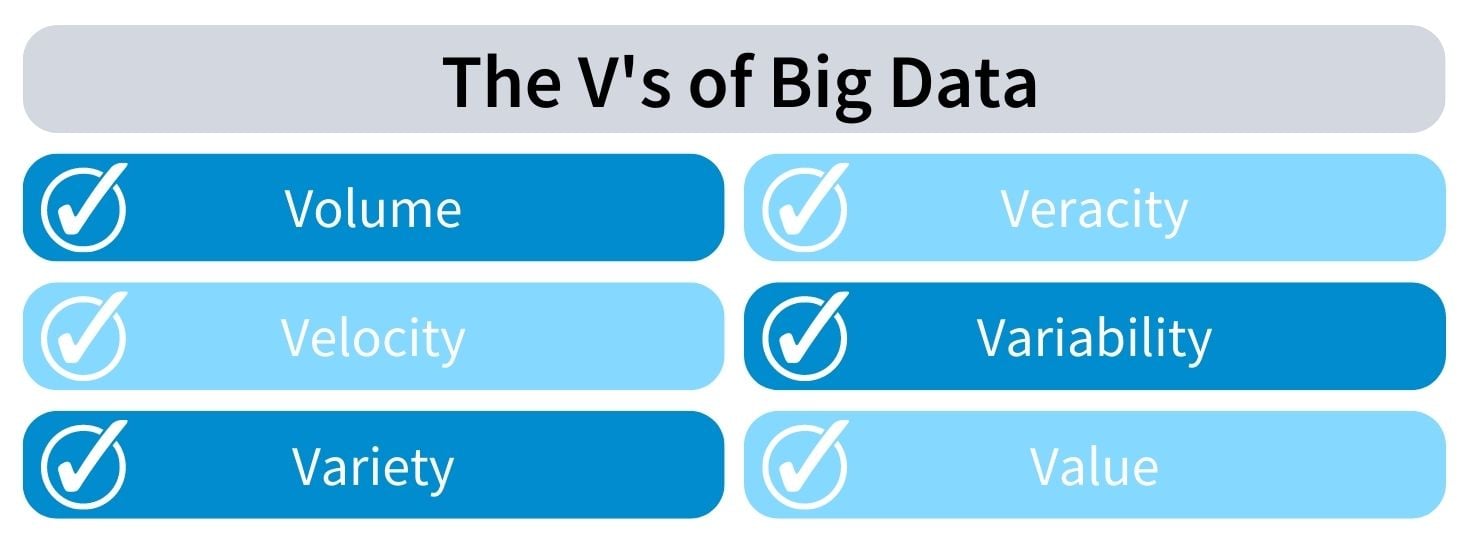
Back in 2001, big data was defined by the three Vs — volume, velocity, and variety. While these three categories are still important, there are new aspects to consider. More recently, leaders in the industry are looking to other categories, such as veracity, variability, and value.
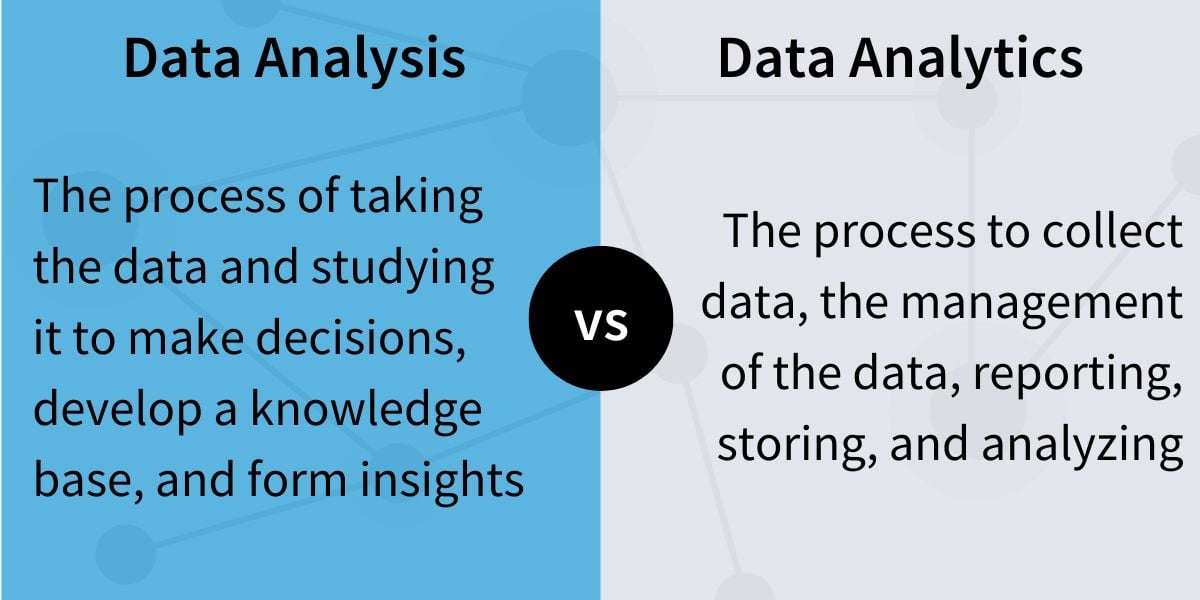
Data Analysis vs Data Analytics
Many of the terms used in data science tend to be used interchangeably, which gets confusing for those just entering the field and those who use data in their specific industries. Let’s start with the definitions to help understand the terms accurately.
The data analysis definition is distinct. It’s the process of taking the data and studying it to make decisions, develop a knowledge base, and form insights. Data analysis deals with finite data sets and may use multiple data sets to develop reports and information about a specific question. For instance, a marketing analyst might use the reporting from multiple channels to determine which campaigns were resulting in the highest traffic. They might then look at which channels resulted in the highest conversion, which might not be the same. Taking all the campaign traffic results into consideration, they would make recommendations on changes to improve the process for the next campaign.
The data analytics definition is slightly different. Data analytics is usually thought of as the whole process for collecting and interpreting data. In this broad definition, data analysis is actually a part of data analytics. Data analytics is also the name we give to the tools used to collect and analyze the data. For instance, Google Analytics is a tool to collect data and help you develop reporting options that allow for better oversight of web properties. Data analytics includes the process to collect data, the management of the data, reporting, storing, and analyzing.
The quality of the data is integral to the success of any data analysis. Companies aren’t only looking for honest and accurate information, but they need access to a wide variety of data in order to create actionable insights. Insights are often formed based on internal and external data which helps them to understand the consumer and their place in the market space.
Data Science Technologies in the Marketing Industry
Data science plays a key role in all business decisions today. Prior to the wide use of digital information, many large scale corporations relied on due diligence to manage and grow their enterprises. This meant a great many man hours and resources that had to be scoured without the aid of automated processes. For instance, purchasing a property would need in depth reporting on the location, the building, the history of the area, etc. If the property was purchased to open a store, market research for that location would be necessary.
In that old scenario, large entities had a major advantage because they had the resources to collect this information, though it was often time consuming. Today, data science is the main method for due diligence and it’s available for every size business, giving small startups a way to compete in a larger market.
Data science is used in every aspect of business, from financial interests such as your revenue cycle through efficiency and management. It is exceptionally useful in marketing and every size business can capitalize on the advantages that data science offers in this area. The definition of data science is the use of data to gain insights, in basic terms. Data science, as a field, encompasses all the facets used in collecting, storing, mapping, and analyzing the information. So it’s an umbrella term with thought leaders who specialize in different areas of data science.
For smaller businesses and those who handle their own marketing initiatives, taking a data science tutorial or regularly expanding your knowledge base in this field is necessary. Data science is how you develop insights by using your interior analytics and data sets from various points. You might, for example, study market research on your specific demographic and then use that data in combination with internal analytics to reach valuable insights that help you engage with your customer base.
As you can see, data science is integral to marketing but it’s also invaluable in every facet of business. It eliminates the need to guess what the market wants because you have access to information about what your customers are really asking for. This knowledge base can be found through internal surveys, competitor information, reviews, and a study of the traffic and engagement through your own social media and website property posts.
Data Science Certification and Job Demand
If you’re considering a data science certification or a data science course, it’s important to know what the career trajectory is for this field. As discussed earlier, data science is a wide field and there is a great need for experts in virtually every industry. A degree in this field will give you marketable skills for the current and future employment market. Of course, there are different specialties within data science which will impact your job responsibilities and earning potential. It’s important that you research the area of data science you’d like to work in to have a full knowledge base of the experience you need and the salary that you can expect in your location.
Demand for data scientists will remain high. This is projected because every industry needs specialists in this field. Though there is an influx of new professionals entering data science, the job growth is not expected to slow down any time in the near future. Those who enter the data science field can specialize in a number of positions, including data analyst, coding, management, and advanced data architecture.
There are a number of different types of positions that you can fill with a data science background. Often, the highest paid data scientists will have advanced degrees, such as a master’s or PhD. There are entry level positions available for those with a bachelor’s degree, as well. To put this in perspective, the median salary for a data scientist is over $113,000 annually. There are those who start as low as $50,000 and those who expect to earn much more. The variables in pay will depend on the type of data science you specialize in, the industry, the location, your education and experience.
Programmers or those who have programming knowledge can expect to make far more than those who do not know how to code. Salary is also dependent on the job title, for instance, those in management make substantially more than say an entry level data analyst. Income level will also often depend on the geographic location and factors such as experience in the industry.
Data scientists work across every industry. Some popular options include marketing, government, software and tech companies, and research and development. If you have a particular interest in a set industry, such as marketing, a good option would be to pursue a data science degree with a minor or double major in that industry. Another option might be to take classes or update your education in that industry so that you have specialized knowledge.
In marketing especially there is a need for professionals who understand both the data science disciplines and the more creative or humanities based influences of marketing. This is key because many marketing professionals come from an arts or English based background. For those with artistic talent, marketing offers a secure professional trajectory but without any analytics background it can be a difficult field.
Often there is a disconnect in marketing between those who develop copy and graphic collateral and those who work exclusively with the analytics. Professionals who can bridge this communication gap are in very high demand and can often command a higher salary. Understanding both of these disciplines allows for a better flow of communication and streamlines the productivity various specialties within the marketing department.
Marketing has a need for various specialties within the data science field. These include analysts, those who work with analytics and develop analytics, those who work with web design and coding, and those who work with a wide array of data sets to develop actionable insights.
Data Analytics Career Opportunities
If you’re looking for data analyst job prospects, the field will continue to grow for the next several years, at least. Data analysts are in high demand, which means that even entry level data analyst jobs can pay exceptionally well. The salary is often dependent on the industry itself.
We’ve discussed data science jobs in marketing. The data analyst salary in this field is also well above the median average salary, though analysts can earn considerably more in fields such as finance. If you’re interested in both finance and computer science, this is an excellent combination. Data analysts are also in high demand across every industry. The market for this type of degree will continue to expand because the amount of data and tools have exploded in recent years, making capable experts a necessity.
Data analysts do well with a background in business, marketing, and finance. The higher paid positions often need an advanced degree but those with a bachelor’s degree can still earn higher than average. The reason analysts are paid so well is because they help businesses with strategy and this is an exceptionally useful skill.
Analysts take data from internal processes and external points and help businesses to see trends, forecast changes, and make a variety of high level decisions that dramatically impact productivity and profitability.
A data analyst who specializes in marketing might develop more accurate customer personas, and go through large swaths of data to interpret the success of branding or campaign initiatives. They use the information culled from various sources to develop insights that can have a dramatic effect on the business, the way it’s viewed, and how far your marketing initiatives can reach. That’s how powerful this specific skill can be.
For business analysts, the workflow can be varied, depending on the industry. The insights often have far reaching ramifications. Solid forecasts can help shareholders make hiring decisions, purchasing decisions, and launch any number of initiatives that will have a marked impact on employees and consumers.
New products are often created using analytics, which has improved the process dramatically. Rather than developing a product and then researching the market, companies are turning the process around so that they’re actually developing a product that their audience already wants. Companies tap into the data in order to see where their target market lives, what their pain points are, and what services or products they can offer that will best serve the end user.
A data analyst has the ability to manage the tools and analytics to collect the best data for the reporting necessary to answer specific quandaries. From there, the analyst can help business leaders find insights and implement the most productive plans to move their businesses forward.
The Role of Analytics in Business
The role of analytics in business is wide and varied. It’s also continually growing. While virtually all businesses have embraced the use of analytics to some degree, many still feel that there is work to be done before they can truly note data analytics success stories. In short, many businesses believe that they are falling short in using the massive amounts of data that they can collect in an efficient or truly game changing way.
This is important to note for future and current data analysts because it means that there will continually be ways to grow in this field and room for innovations. Analytics are used in every department and the best analysts also understand how to incorporate the internal data with external sources to bring forth insights that create new business opportunities and growth potential.
The scope of data analytics is mind boggling. Take any business model and you can see data being used in all of the facets of the industry. Take manufacturing, for example. Data sets can be used to improve production, cost efficiency, hiring and employee management, packaging, shipping, content management, marketing, and accounts payable and receivable. Not only that, but data analysis is used to bring forth new innovations in the whole operational experience.
The analytics give businesses advanced tools to determine whether they need to make changes and what potential payoff they can expect from their investment. Of course, analytics can’t without flaw fully predict the future. But the data, when analyzed effectively, can give businesses great foresight into their decisions.
This works as a sort of security measure. There is always some risk involved in business investments of any type. But the risk in unknown variables is always higher because there’s simply no way to research in advance. Great analytics can provide insights into possible opportunities to grow business and change offerings.
In the marketing space, data analytics tools help analysts build robust marketing attribution data models and marketing plans that incorporate all the channels where your audience will find your brand. A solid content marketing strategy might include the way that the brand functions from brick and mortar through digital contact points. All of this data combined helps to develop a full picture of the individual customer.
Data analytics are increasingly important because every other company is using their own data and tools such as AI, automation, and a variety of sales and marketing content management systems to help propel their messaging and understand their demographic. What this means for the individual company is that not taking full advantage of the analytics leaves you far behind the competition.
Analytics propels business intelligence, or BI. Business intelligence is the use of big data to inform all facets of business decisions, from products to branding to the type of service that’s offered. As companies invest more time and money in the data analytics tools and platforms to help them gather, save, and assess the massive amounts of information at their fingertips, they’re looking for ways to fully profit from these initiatives.
While you’ll hear tools and platforms referred to as data analytics, the term also encompasses the process of how this information is gathered and the strategy to use it effectively. With a great deal of data there is a bigger need for strategic planning to make this information fully useful. Without paying attention to the insights, it’s ineffective to collect or store data because it simply has no payoff. For the process to reap results, the data itself needs to be analyzed and put into action. This process can be completed in every division of a company, as well as an overall strategy for the whole business model and administrative workflow.
Resources
Channel Optimization
Consumer Behavior
Consumer Insights
Consumer Insights and Analytics
Competitor Analysis Tools
Content Marketing
Content Strategy
Cross-Channel Analytics
Customer Insight Research Techniques
Customer Journey Map
Market Intelligence
Marketing Analytics Techniques
Market Research
Marketing Attribution
Opportunities of Internet Marketing
Types of Consumer Insights





