8 Step SEO Content Checklist
Search engine optimization (SEO) has been a key marketing strategy for content marketers for a while now, but knowing exactly how to get it done is a constant struggle for many. Deciding what to write about, organizing website structure, and publishing content while following the latest best practices can feel like more than a full-time job.
That’s why we at DemandJump wanted to give you clear and easy-to-follow SEO checklists to get you started on the right path. After all, using the right SEO content tools will make your job a lot easier, especially when in tandem with a content optimization strategy.
What Does SEO Content Include?
SEO content includes anything on your website that is crawlable (or easily accessible) by search engines that has the potential to increase your rankings in search engines results pages (SERPS). This means that pretty much every word written on your website can be considered SEO content, as well as images, graphics, and even the URLs you choose for each page.
For this article, we are mostly going to focus on long-form content like Supporting Blog posts or even longer articles. We’ll cover how to create your own SEO checklists that fit your needs best and take you through planning, writing, and publishing these articles.
We’ll also touch on some of the other forms of SEO—like on-page and technical—and provide checklist template resources for them as well. Buckle up for our ultimate SEO checklists!
How Do I Create an SEO Checklist for Content?
The first thing on your checklist should be to… create your checklist! You can certainly Google “SEO checklist for blog posts” and find a premade template (and we’ll give you one here too), but every company is going to have different structures, goals, timelines, and resources as part of their individual SEO content writing guidelines.
For instance, you might be working with a well established website with lots of high-ranking content, and just need an SEO maintenance checklist to keep it performing well. Or you could be creating a brand new website for a startup that doesn’t have any content at all—so you’d want an SEO checklist for a new website. Creating your own checklist or tweaking an existing one will give you a customized approach that will work the best for your exact situation.
Let’s jump into creating checklists to see exactly how they can work for you. We’re going to break the process down into four parts: creating the structure, writing the content, publishing, and then checking your on-page and technical SEO.
Let’s jump into creating a checklist to see exactly how it can work for you. We’re going to break the process down into three parts: creating the structure, writing the content, and publishing.
For more great SEO content nuggets subscribe to Page One or Bust! wherever you listen to podcasts.
Part One: How Do You Structure SEO Content?
Before you write a single word, you need to decide how you are going to structure the articles. Creating a reliable and valuable SEO content strategy does not mean choosing topics at random or based on your gut feeling about what your customers might want to read.
To really succeed at SEO today, you need a concrete plan for choosing topics based on data and structuring articles in a way that shows search engines your website is a topical expert.
Here’s an example checklist for creating the structure for your SEO content:
Step 1: Choose a method of structuring. This might include things like:
- Researching different blog structure options for SEO success (we recommend a Pillar-Based Marketing (PBM) structure—more on this later).
- Considering what structure you already have in place if you are working with existing website content.
Step 2: Decide what tools you will use to create and plan your structure. This will involve:
- Choosing a keyword or topic research tool, like DemandJump.
- Considering who will be responsible for creating the structure and writing the content.
- Thinking about the timeline and resources available for actual writing.
Step 3: Map out your structure, including the titles of each article you plan to write and how each will fit into the overall content plan you develop.
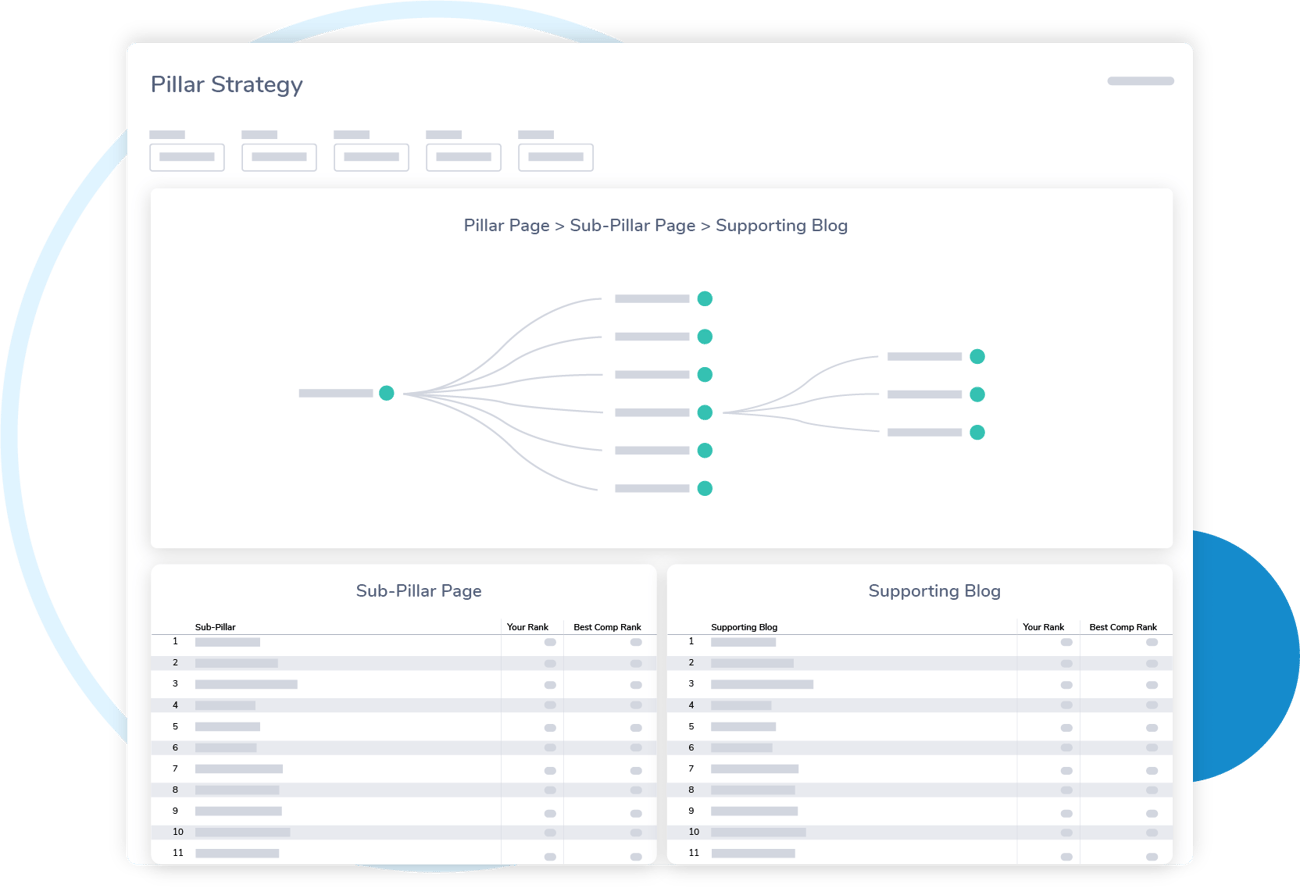
So what might these steps look like in the real world? The most effective and data-backed approach to creating this type of structure is Pillar-Based Marketing. To get started, you choose an overall topic you want to rank highly for.
Let’s use a hypothetical example: a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) company called DinoSore that connects schools and daycares in need of medical supplies with hospitals and other donors that can provide them. DinoSore might choose the overall topic—called a “Pillar”—of “School Medical Supplies”. That’s the phrase they want to rank for the most.
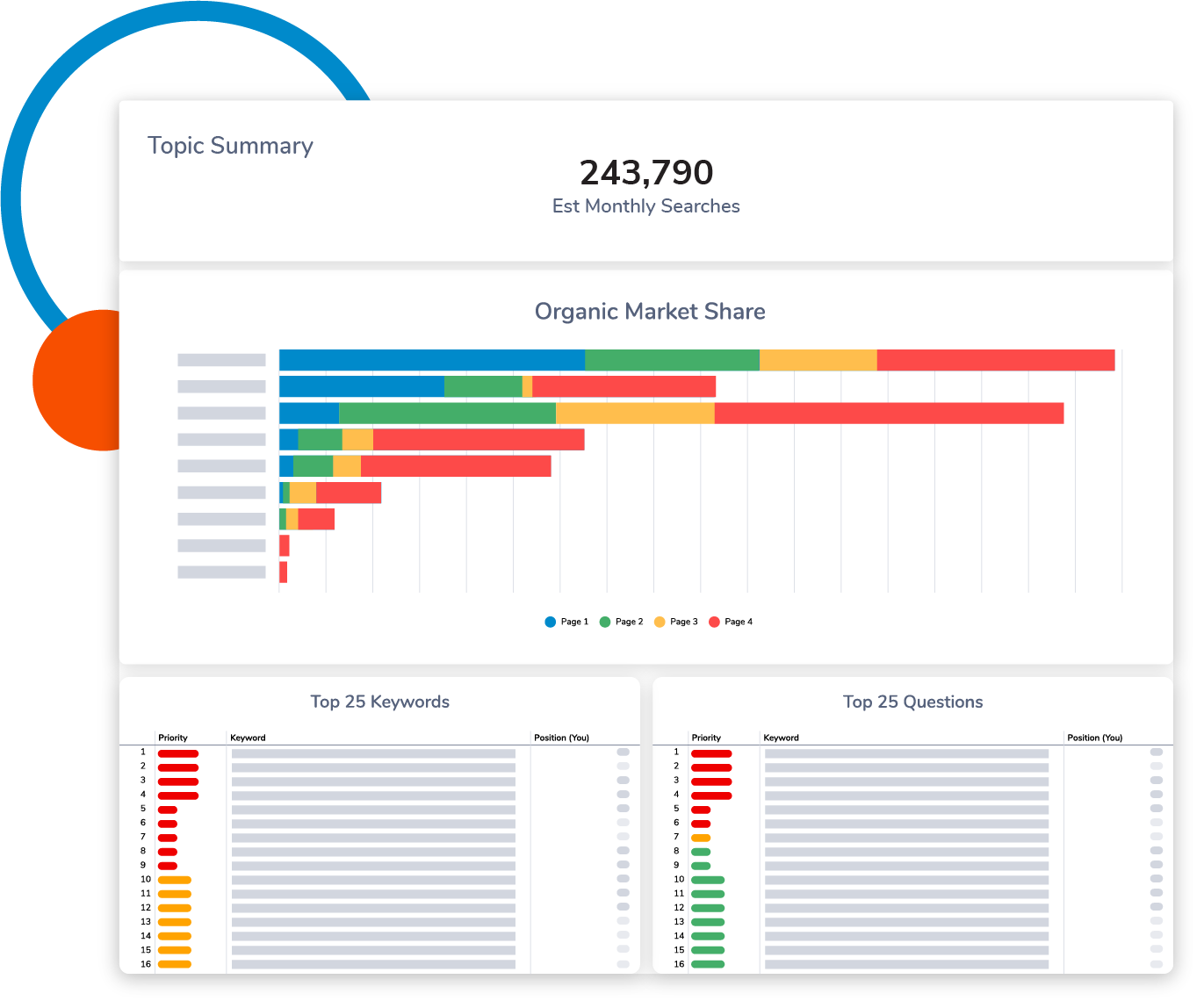
Using PBM, DinoSore would then create the structure of the rest of their Supporting Blogs by coming up with other article titles that fit under this main Pillar. A PBM platform, like DemandJump, will show which related topics people are searching for around this Pillar, so the rest of the content can be planned out.
This is what an example plan might look like for their “School Medical Supplies” Pillar.
/content-pillar-example.jpg?width=719&height=540&name=content-pillar-example.jpg)
Part Two: How Do You Write Content for SEO?
Once you have the structure set for your SEO content, it’s time to start writing. Here is an example of a checklist you should use during the writing phase:
Step 1: Assign the writing tasks. In a small team, the whole process of planning, writing, and publishing might be carried out by just one person. It could also be split up amongst an entire marketing department, or outsourced to third party content writers, like those on the DemandJump content team.
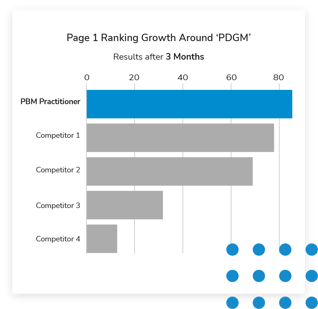
Step 2: Set a realistic timeline. Once you know who is responsible for doing the writing, you can set reasonable deadlines for them to finish each piece that works with their bandwidth and the schedule you would like to release the articles. An example timeline for our hypothetical company DinoSore might look like this:
/seo-content-timeline.jpg?width=600&height=451&name=seo-content-timeline.jpg)
Step 3: Write the longest, broadest, most important piece of content first. If you're using a PBM structure—like our example DinoSore—this means writing the Pillar page first. Our hypothetical business would first write a 3,000-word article covering all the basics of School Medical Supplies.
Step 4: Review and get approval on this most important content piece | Before anyone keeps writing more content, make sure all the important stakeholders review and approve the first piece. Getting buy-in at this stage will save headaches later on, as all the Sub-Pillars and Supporting Blogs must align with the main Pillar to ensure consistency across your website.
Step 5: Write the second tier of content, the mid-length articles | In PBM, these are called Sub-Pillars and are about 2,000 words long. They have slightly longer titles than the Pillar, and explore specific elements of the main topic in more detail. A Sub-Pillar topic for our DinoSore company is “Free Adhesive Bandages for Kids”. A complete Pillar plan will have at least three Sub-Pillars under each Pillar, and ideally you would write all the Sub-Pillars before you move on to the next step.
Step 6: Review and get approval on all the mid-length articles | Just like with the largest piece of content, you want to make sure that the information in these more detailed pieces of content are correct and approved by key stakeholders before you continue writing the most detailed pieces—Supporting Blogs.
Step 7: Write the shortest, most in-depth blogs | In PBM, these Supporting Blogs will have long-tail questions as their titles and will drill down into very specific questions your audience is searching for. Each Supporting Blog should be about 1,000 words, and there will be at least three Blogs under each Sub-Pillar topic.
Step 8: Review and get approval on all Supporting Blogs | Send your last set of articles through the same approval process as before. Since the important stakeholders have already reviewed and approved the higher-level pieces, these blogs should go smoothly too.
Phew—now that all the hardest writing work is finished, it’s time to get the content out into the world so it can start working its SEO magic!
Bonus SEO Checklist: What Are the 4 Important Stages in SEO?
The four important stages of SEO are:
 Stage One: Keyword Research. In order to show our search engine overlords that you know what you’re talking about, it’s vital to include relevant keywords and cover as many of the questions that people are asking about your chosen topic. Using a platform like DemandJump makes this stage a breeze!
Stage One: Keyword Research. In order to show our search engine overlords that you know what you’re talking about, it’s vital to include relevant keywords and cover as many of the questions that people are asking about your chosen topic. Using a platform like DemandJump makes this stage a breeze!
 Stage Two: Readability Check. Google prioritizes clear, concise, helpful content. Make sure you’re following best practices like:
Stage Two: Readability Check. Google prioritizes clear, concise, helpful content. Make sure you’re following best practices like:
- Incorporating white space through paragraph breaks
- Using bullet points and lists to make content skimmable
- Inserting headers so that people can quickly jump to the sections they want to read
 Stage Three: Linking. To help establish your content as authoritative, you should use both external and internal links to signal your expertise. You can learn more about PBM linking in the article linked above!
Stage Three: Linking. To help establish your content as authoritative, you should use both external and internal links to signal your expertise. You can learn more about PBM linking in the article linked above!
 Stage Four: Marketing. After you’ve posted your content, it’s important to include some marketing aspects. Using social media and paid ads can give your content the boost it needs to gain traction.
Stage Four: Marketing. After you’ve posted your content, it’s important to include some marketing aspects. Using social media and paid ads can give your content the boost it needs to gain traction.
Part Three: How Do You Publish Content for SEO?
Once you have all of your content written, it’s time to get it up on your website. There are some specific publishing guidelines for PBM and structured content releases that you want to follow for the best results. Here’s a short checklist to help you get through it:
 Publish Everything At The Same Time. Yes, you read that right! PBM best practices recommend publishing everything—all Pillars, Sub-Pillars, and Supporting Blogs— all at once. In our experience at DemandJump, this huge injection of content onto your site jolts search engines to recognize your content as new, index it quickly, and rank it highly.
Publish Everything At The Same Time. Yes, you read that right! PBM best practices recommend publishing everything—all Pillars, Sub-Pillars, and Supporting Blogs— all at once. In our experience at DemandJump, this huge injection of content onto your site jolts search engines to recognize your content as new, index it quickly, and rank it highly. Check Your On-Page SEO. Be sure to set up your page for success by optimizing the on-page elements for search engines. Wondering how to do this? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered with a checklist in the next section!
Check Your On-Page SEO. Be sure to set up your page for success by optimizing the on-page elements for search engines. Wondering how to do this? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered with a checklist in the next section! Keep Up With Off-Page SEO. Make sure you’re covering your bases through strategies like social media campaigns or soliciting positive reviews. We’ve got a brief guide to help you understand off-page SEO better.
Keep Up With Off-Page SEO. Make sure you’re covering your bases through strategies like social media campaigns or soliciting positive reviews. We’ve got a brief guide to help you understand off-page SEO better. Check Your Technical SEO. You may need to work with your IT team or webmaster to make sure your site is in tip-top technical shape. And yes, we’ve got a checklist for technical SEO coming up in this guide too.
Check Your Technical SEO. You may need to work with your IT team or webmaster to make sure your site is in tip-top technical shape. And yes, we’ve got a checklist for technical SEO coming up in this guide too.
Now that you have published all the content around your chosen topic, it’s time to watch your search engine rankings take off!
Part Four: How Do You Do On-Page and Technical SEO?
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing the content and structure of each individual web page to make them more appealing to users and search engines. Meanwhile, technical SEO dives into the more complex backend elements to make sure your site is crawlable, fast, and secure. Together, these two SEO techniques work together to bring in (and keep!) your target audience and boost your ranks on the results page. Let’s take a look at each—with checklist resources—to help you understand how to accomplish both on-page and technical SEO.
What Is a List of 5 On-Page SEO Techniques?
On-page SEO is about making sure everything on a web page is optimized for search engine ranking. This means having the good and helpful content you’ve just written, but also involves elements like:
- High Quality Content: Providing well-written, informative content that follows Google’s E-E-A-T principle will help boost your on-page SEO. Be sure to cover each topic comprehensively, giving well-researched information that is tailored to your target audience’s interests and queries. (Hint: Don’t forget that you can use DemandJump to find the exact keywords and questions that people are searching for around your topic!)
- =Meta Descriptions and Title Tags: These critical HTML elements help users and search engines understand what content is on your page. Both should be engaging and educational, encouraging users to click your link.
- URL Structure: An excellent URL is concise, includes keywords, and is easy for users and search engines to grasp. It should reflect the hierarchy of your website and avoid excessive length or complexity. Including a clear URL structure enhances the user experiences as well as supports search engines in page categorization.
- Internal Linking: Be sure to follow PBM linking guidelines to help users and search engines find more of your quality content!
- Image Optimization: Using alt tags and optimizing file sizes for images helps make your content more accessible for users and assists search engines with understanding the image content. This helps boost your page’s SEO.
Free SEO Checklist: What Should Be Included on an On-Page SEO Checklist?
Here’s one example of the on-page SEO steps your checklist could include:
 Step 1: Go through each web page and make sure there are at least three high-quality images.
Step 1: Go through each web page and make sure there are at least three high-quality images. Step 2: Provide alt text descriptions for each image using high-value keywords that describe the image well.
Step 2: Provide alt text descriptions for each image using high-value keywords that describe the image well. Step 3: Review your internal linking strategy. One of the goals of PBM is to show search engines that your Pillar page is the main topic authority on your chosen topic. Linking each Supporting Blog and Sub-Pillar up to your Pillar is a great way to do that.
Step 3: Review your internal linking strategy. One of the goals of PBM is to show search engines that your Pillar page is the main topic authority on your chosen topic. Linking each Supporting Blog and Sub-Pillar up to your Pillar is a great way to do that. Step 4: Check your article titles. Each web page should have the high-value keyword you selected formatted as the title. This makes it easy for search engine bots (or crawlers) to understand what topics the page covers.
Step 4: Check your article titles. Each web page should have the high-value keyword you selected formatted as the title. This makes it easy for search engine bots (or crawlers) to understand what topics the page covers. Step 5: Ensure each page has a meta description that clearly explains what the piece is about. This description should include most of the words from the title and be 145-155 characters long.
Step 5: Ensure each page has a meta description that clearly explains what the piece is about. This description should include most of the words from the title and be 145-155 characters long.
What Does Technical SEO Include?
Technical SEO deals with improving your website’s foundation and backend structure. An example of technical SEO is proactively managing your 404 error pages and setting up 301 redirects properly. This ensures that users and search engines are guided to the correct page when they accidentally stumble on an area of your website that is under construction.
What Is a Technical SEO Checklist?
A technical SEO checklist should include elements like:
 Mobile Responsiveness: With mobile devices driving a significant portion of web traffic, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly will help boost your SEO results. Search engines prioritize mobile-responsive sites in their rankings, so make sure your page fits this criteria!
Mobile Responsiveness: With mobile devices driving a significant portion of web traffic, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly will help boost your SEO results. Search engines prioritize mobile-responsive sites in their rankings, so make sure your page fits this criteria!
 Website Speed Optimization: You know how frustrating it is when a webpage just won’t load! No one wants to see that spinning circle, and search engines know this. They tend to reward pages that load quickly since this provides a better user experience.
Website Speed Optimization: You know how frustrating it is when a webpage just won’t load! No one wants to see that spinning circle, and search engines know this. They tend to reward pages that load quickly since this provides a better user experience.
 Easy Crawlability and Indexing: It’s vital to manage robots.txt files and sitemaps to make sure that search engines can properly crawl and index your website.
Easy Crawlability and Indexing: It’s vital to manage robots.txt files and sitemaps to make sure that search engines can properly crawl and index your website.
 Logical Site Architecture: If your page isn’t set up with a logical structure, search engines (and users!) will have difficulty understanding how to navigate. This can negatively affect your SEO. On the flip side, having a clearly organized site structure can help boost your rankings!
Logical Site Architecture: If your page isn’t set up with a logical structure, search engines (and users!) will have difficulty understanding how to navigate. This can negatively affect your SEO. On the flip side, having a clearly organized site structure can help boost your rankings!
 Secure Connection: It’s important to implement SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) for a secure, HTTPS-encrypted connection—not only for the sake of protecting your users, but also as a best practice to optimize your SEO rank.
Secure Connection: It’s important to implement SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) for a secure, HTTPS-encrypted connection—not only for the sake of protecting your users, but also as a best practice to optimize your SEO rank.
What Is The Best SEO Tool to Use? DemandJump!
With our platform, you’ll have easy SEO content creation at your fingertips. After all, is there anything more tedious than researching keywords and trying to figure out how to get your content to the top of page one? Here at DemandJump, we’ve changed all that for you. With our SEO content platform, you’ll be able to quickly and easily find the keywords and questions that your target audiences are searching for. Get started on your journey to page one today!








/content-pillar-example.jpg?width=719&height=540&name=content-pillar-example.jpg)
/seo-content-timeline.jpg?width=600&height=451&name=seo-content-timeline.jpg)